Why America Has Such A High Rate Of Payment-Card Fraud
February 19, 2014 Leave a comment
Why America Has Such A High Rate Of Payment-Card Fraud
THE ECONOMIST RETAIL FEB. 15, 2014, 3:25 AM
AMERICA leads the world in many categories: shale-gas production, defence spending, incarceration rates and, alas, payment-card fraud. In December Target, an American retailer, said that hackers had breached its network and stolen payment-card details of about 40m of its customers.
A few months before the Target breach, roughly 152m customers had their information stolen in a hack of Adobe Systems. Last month Neiman-Marcus, a department store, reported a similar breach.
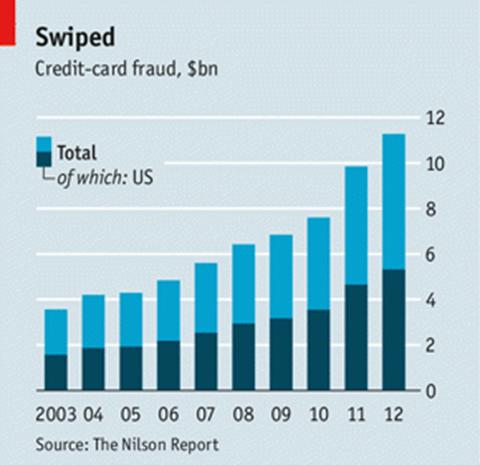
For crooks, there are rich pickings in such data. Total global payment-card fraud losses were $11.3 billion in 2012, up nearly 15% from the prior year. The United States–the only country in which counterfeit-card fraud is consistently growing–accounted for 47% of that amount, according to the Nilson Report: card issuers lost $3.4 billion and merchants another $1.9 billion.
A survey released in 2012 by the Aite Group and ACI Worldwide, a research and a payment-software firm respectively, found that 42% of Americans had experienced some form of payment-card fraud in the preceding five years. Nor is it just Americans who are affected: foreigners whose card data is stolen often find the thieves have little trouble waltzing into stores and making purchases with ersatz cards. Europeans rack up more losses in this way in America than in any other country.
In part, fraudsters target the United States because that’s where the cards are. At the end of 2013 there were 1.2 billion debit, credit and pre-paid cards in circulation in America–more than in any other region. That is nearly five cards per adult.
But America also makes things easy for fraudsters: alone among developed countries, it still relies exclusively on cards with magnetic strips, which are far less secure than the chip-and-PIN technology used elsewhere. This combines a personal code with a microchip from which it is harder to extract data than a magnetic strip.
As of 2012, 45% of the world’s payment cards and 76% of terminals were equipped to use chip-and-PIN. By 2011 this technology had brought some forms of card fraud in Britain to their lowest level in two decades. The spread of chipped cards in Canada brought losses from skimming–stealing data from credit cards–from C$142m ($129m) in 2009 to C$38.5m in 2012.
At a series of Senate hearings earlier this month, Target’s CFO said it would spend $100m to roll out chip-and-PIN store-issued credit cards and payment devices that accept them. A consumer advocate urged other card issuers to do the same. Though the switch may cost issuers and merchants as much as $8 billion, interest at long last appears to be growing.
Many of those costs may be recoverable over time through lower fraud losses. Chip-and-PIN would also harmonise American and global standards, making it easier for Americans to use their cards abroad and foreigners to use theirs in America. It will make mobile payments easier. And because recent banking regulations have reduced the amount of money banks make from interchange fees on debit cards, issuers are looking to trim costs elsewhere. Fraud losses no longer seem as manageable as they once did.