A world of robber barons: The relationship between business and government is becoming increasingly antagonistic, says Philip Coggan. But the two sides should not overdo it: they need each other
February 27, 2014 Leave a comment
Companies and the state
A world of robber barons: The relationship between business and government is becoming increasingly antagonistic, says Philip Coggan. But the two sides should not overdo it: they need each other
Feb 22nd 2014 | From the print edition
IN THE MIDDLE AGES the Rhine was Europe’s most important commercial waterway. Like many modern highways, it was a toll route. Toll points were meant to be approved by the Holy Roman Emperor, but local landowners often charged river traffic for passing through. These “robber barons”, as they became known, were a serious impediment to trade, and imperial forces had to take costly punitive action to remove them.
The relationship between business and the state bears some resemblance to this medieval tussle. Like those Rhine boatmen, the companies operating within national borders must pay something towards the cost of supporting commerce, but if the tolls are excessive, trade will suffer. At least some of the world’s 200 or so countries will be tempted to act as robber barons, charging the equivalent of protection money to the companies they deal with.
Some people on the left would argue that the label should be applied in the opposite way. In the late 19th century the term “robber barons” came to refer to the American railway magnates who used their monopoly power to drive competitors out of business. Politicians such as the trustbusting presidents Theodore Roosevelt and William Howard Taft crusaded against such corporate power.
Since then that anti-corporate mood has never quite dissipated. Modern multinationals are sometimes portrayed as overmighty, using their wealth to subvert politicians through their campaign contributions and lobbying power and to evade their social responsibility.
Much political rhetoric across the spectrum suggests that the relationship between companies and the state is in essence antagonistic. Those on the right argue that government interferes far too much in the process of wealth generation and hinders rather than helps commerce. Those on the left depict business as a ravenous predator that government needs to control, exploiting workers and consumers and evading taxes.
All that combative talk made it harder to respond to the 2007-08 banking crisis. The collapse of the subprime-mortgage market and the subsequent rescue of the banking sector created a sense of anger towards the financial elite which turned into a wider frustration with the corporate world. The crisis led to a plunge in tax revenues and a sharp rise in budget deficits, prompting governments to pursue austerity programmes that imposed tax increases on many middle-class people and cut the benefits of the less well-off. Such a climate breeds resentment of companies that are seen as not paying their fair share of taxes or of exploiting their monopoly pricing power.
Perhaps the trickiest relationship at present is between governments and the technology industry
In response, governments have introduced strict new regulation, particularly for banks, and sought to crack down on the use of offshore tax havens. But they have also recognised that they cannot afford to drive multinational business away. Some countries, including Britain, have cut their tax rates in order to attract new business from abroad. “Countries have got to see themselves as being an attractive shop window for multinational investment,” says John Cridland, director-general of the Confederation of British Industry. Even France’s president, François Hollande, who in 2012 came into office on a wave of anti-capitalist rhetoric, last month announced a €30 billion ($41 billion) cut in corporate taxes in an attempt to revive a stagnant economy.
For all their differences, the two sides need each other. Governments rely on businesses to drive economic growth, create jobs and generate the exports to ensure that their countries can pay their way in the world. Multinationals are particularly important, argues Ted Moran of the Peterson Institute for International Economics, an American think-tank: they pay higher wages than other companies, export more and have a superior record in research and development. And countries would be unwise to rely on multinationals staying put come what may: WPP, an advertising and marketing group, moved its headquarters from London to Dublin in 2008 in a dispute over tax on overseas profits, then moved it back again after the rules were changed. With growth in emerging markets so much faster than in the developed world, locations like Singapore or Dubai are becoming ever more attractive.
Businesses, for their part, need governments. It is not just that they provide the legal systems and the basic security that allow companies to operate in the first place; they also educate the workers on whom firms depend, and they create the infrastructure—roads, railways and air-traffic control—that enables companies to get their goods to market. Moreover, governments undertake a lot of scientific research that businesses can turn into commercial products, from the internet to satellite positioning systems to drug development.
In many industries the government is also a key customer; after all, a typical government in a developed country spends around 40% of GDP. Defence is an obvious example, but the pharmaceutical industry is also important: national health services are huge buyers of drugs, and government bodies have to approve new products before they come to market. Construction, too, depends heavily on government action: a boost to infrastructure spending can make a big difference to the industry’s prospects.
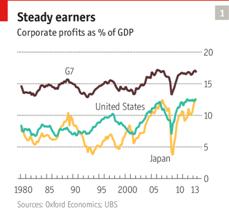
Government policy also has serious (and sometimes unintended) effects on corporate structure. In America, high corporate taxes and a growing body of regulation have led to a decline in the number of public corporations and the emergence of alternative structures such as “master limited partnerships”. Around the world, the tax deductibility of interest payments has encouraged a greater reliance on debt rather than equity and favoured private-equity firms. Even though executives moan about excessive government interference, shares on Wall Street have been hitting record highs, and profits as a share of America’s GDP are close to a post-war high.
Because of the sheer scale of the modern state, companies are obliged to engage with it on many levels. Governments, for their part, are expected to deal with a variety of ills in society, from banning imports of unhealthy or dangerous substances to combating global warming.
You know too much
Perhaps the trickiest relationship at present is between governments and the technology industry. Some consumers are uneasy about the large amount of digital data being hoovered up and want governments to regulate the way that businesses use and maintain these data. The governments’ security services, for their part, want to have access to such information whenever they feel the need. Recent revelations about the extent of government monitoring of e-mails and phone calls have pushed this issue into the headlines and created a dilemma for tech companies. Do they stand up for their customers and risk being accused of compromising security, or do they give in to governments and risk alienating their customers?
Another set of complications arises from social benefits for citizens provided jointly by companies and governments. In health care, for instance, many small businesses think that America’s Affordable Care Act imposes an excessive administrative burden on them. Parental leave also divides the spirits. Many governments want to extend maternity leave for women and offer parental leave to fathers. That may be manageable for big businesses but is harder to implement for small companies. Given that voters are resistant to higher taxes, politicians are drawn to programmes that offer improved benefits at the expense of companies rather than the state.
Big businesses accept that they need a relationship with government. That has fuelled the rise of the lobbying industry and, in some countries, the growth of campaign contributions by firms. Many people now suspect that the key to success in business is not necessarily to be the most competitive but the best-connected. Lobbying creates a kind of arms race in which tax laws and regulations become ever more complex as companies seek to influence the rules to suit their own interests.
Favoured firms can be “national champions”, such as airlines, which governments strive to protect through regulation and restrictions on foreign ownership. In international trade negotiations they often try to protect the interests of a vital industry, as France does with agriculture and Britain with financial services. In emerging markets such practices are even more entrenched. In some industries, such as energy, Western multinationals find themselves at a disadvantage in their dealings with state-owned titans, as BP found in Russia.
This special report will concentrate on the relationship between business and state in the rich world, which in the aftermath of the financial crisis is clearly under strain. It will consider the role of tax, regulation and competition policy, explain why the technology industry is a special case, examine the arguments for and against lobbying and give examples of how the relationship can be managed successfully.
Redefining the relationship
Partners not enemies
Why companies and governments need each other
Feb 22nd 2014 | From the print edition
UNDER THE FEUDAL system of the Middle Ages, everybody knew their place, even if they occasionally overstepped the mark. The peasant owed allegiance to the squire, the squire to the nobleman and the nobleman to the king. By contrast, since industrial capitalism has been around, the relationship between companies and the state has been volatile. The 19th century was an era of laissez-faire, but in the 20th century two world wars required strong state control of the economy, and in the social democracies that prevailed after 1945 the private sector played a diminished part, particularly in Europe. When economies were liberalised after 1980, the state retreated again and nationalised industries were returned to the private sector.
Now three factors are at work that could change the relationship yet again. The first is the financial crisis of 2007-08, which undermined the argument that free markets, left alone, would regulate themselves. It has been followed by a long period of austerity that has made voters angry and boosted support for populist parties on both left and right. Companies make obvious targets for such popular anger.
factor is the growth of the internet, which has made it much easier for both companies and the state to gather large amounts of information about individuals. The state is tempted to take advantage of this corporate knowledge, largely for policing and anti-terrorism reasons, but also feels the need to regulate how companies store and use personal data.
The third is the continuing impact of globalisation. This gives multinational firms more freedom to move around the world, but it also means that Western companies face competition from many emerging-market titans with state backing. If rich-world governments hobble their own companies too much, they may hand market dominance to the champions of the emerging world. That is no way to create jobs.
There is a fine line between creating an environment in which companies can flourish, and cosseting businesses so much that they become uncompetitive. The problem in developed countries has not, in recent years, been governments’ unwillingness to help; it has been a lack of strategic vision. There has been too much micromanagement to encourage particular industries and particular behaviour.
Don’t chop and change
Time and again, business leaders say that what they want most is consistency. When they make a 15-year investment, they want to be sure that the taxes and regulations at the end of that period will still be the same as at the start. Fiddling with the rules leads to uncertainty, which discourages investment.
The endless tinkering by politicians also leads to a lobbying arms race in which the winners are not the best companies but those with the best political connections. Once caught up in this race, businesses find it hard to quit. And the public comes to believe that the system is rigged in favour of insiders, increasing its resentment of companies. To reduce the need for lobbying, governments should establish a sound basic framework of simple taxes without loopholes, as well as regulation that concentrates on the big picture.
On the tax front, it seems unlikely that the profits levy will disappear altogether in the foreseeable future, but international competition and the increasing popularity of alternative corporate structures such as partnerships are likely to exert downward pressure on tax rates. Companies will always try to manage their affairs so as to minimise their tax bills, but at a time when voters are feeling the pinch, sensible businesses will realise that if they overdo the tax avoidance they might damage their reputation. Governments should focus more on income and consumption taxes, which are easy to define and relatively cheap to administer. The point is not to maximise the revenue from any specific tax but to extract the maximum tax revenue at the lowest cost.
The most difficult area to forecast is technology. In the past 20 years huge tech companies have emerged from nowhere; some, such as Facebook, have created communities that sometimes seem like alternative worlds. The continued growth of online trading, and the creation of electronic currencies such as Bitcoin, have conjured up dreams of a libertarian system out of the state’s reach. At the same time the widespread use of instant-communications systems such as Twitter has created a challenge for businesses: news of a faulty product or poor handling of a customer complaint can flash round the globe in minutes.
Globalisation, too, will remain a disruptive force. Just as governments can find their fiscal position undermined by companies shifting domicile, individual businesses can find their brand undermined by the emergence of new competitors, changes in taste or even political turmoil.
All governments and companies are at the mercy of these long-term trends. In the developed world, businesses are competing against companies from emerging economies that may be directly state-owned or at least have a lot of government support. Economic growth is faster in emerging markets, so that is where multinationals increasingly want to be; if rich-country governments over-regulate their domestic markets, they will get a progressively lower share of multinational investment. Investors in the rich world are more likely to prosper if big companies can take advantage of opportunities in developing countries; as the populations of rich nations age, their pension funds need to accumulate claims on emerging markets.
Leaders on both sides should realise that an antagonistic relationship is in nobody’s interest. Governments lose out if businesses find it hard to operate in their country, and businesses suffer if governments are not able to prevent political or financial turmoil. Governments need to focus on the big picture—in essence, provide a stable tax regime and an education system that produces well-qualified knowledge workers—rather than try to micromanage businesses through excessive regulation. Companies must understand that if they push tax avoidance too far they will alienate customers and undermine the societies in which they operate. At a time when the rich world is struggling to generate growth, governments and companies alike should acknowledge the fact that they are partners not enemies.